User interface/user experience design is one of the trending topic in technology today. But what exactly is it? What is the difference and similarities between them? we’ve created this guide. In it, we’ll walk you through the following areas to explain a clear understanding of UI and UX design.
Table of contents:
- UI Design – How Things Look
- What are the different types of UI?
- UX Design – How Things Work
- What Are the Key Differences Between UI and UX Design?
- What does a UI designer do?
- What does a UX designer do?
- What skills do UI designers need?
- What skills do UX designers need?
- How Do UI/UX Designers Work Together?
- What are FAQs about UX/UI design?
UI Design – How Things Look
A UI (User Interface) deals with the application’s graphical layout, which includes buttons, screen layout, animations, transitions, micro-interactions, and other visual elements. In fact, you are using UI right now to read this article right now.
For good UI design, you should take these characteristics into consideration:
The design should be focused on helping users complete tasks quickly with minimum effort. Completing tasks should be a seamless experience.
It should be enjoyable, satisfactory, and free from frustration.
The UI design should communicate the brand value of the company/organization.
What are the different types of UI?
There are many several types of user interface. Here are the three most common UIs – command line interface, graphic user interfaces, and voice-enabled user interface.
Command-line interface
People can interact with computers using command line interface. The interactions were linear – the user (‘operator’) typed a command, and the machine responded to the command either using printed output or by displaying a message on the monitor. Because users have to know the machine language to interact with computers, the complexity of such interaction was pretty high. It’s nothing new. In fact, it’s the way early computers were used.
Graphical User Interface
The graphical user interface (GUI) is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with digital products through visual elements. When users interact with GUI, they go through a series of pages or screens. Those pages/screens contain static elements (such as text sections) and active elements (such as buttons, scroll bars and other interactive controls). Nowadays GUI is most common type of UI for digital products.
Voice-based interfaces
Voice-based interfaces (also known as VUIs, voice user interfaces) permit users to interact with a system through voice or speech commands. Recent advances in natural language processing made it possible to create products like Amazon Alexa, Apple’s Siri, and the Google Assistant. Voice-based interfaces are becoming more popular and have a low learning curve because they require less time spent learning how to use them.
UX Design — How Things Work
UX (User Experience) design deals with how users interact with the system. Logical navigation and how smooth and intuitive the experience is all fall under UX design. In short, this type of design helps users have a positive experience.
Interaction Design deals with how users can complete their tasks effortlessly by using the interactive components of a system (page transitions, animations, buttons, and so on).
For good UX design, you should follow these practices:
The product should be easily usable, logical, and self-explanatory.
The product should solve users’s problems.
The product should be accessible and usable to a wide range of people.
The product should create a positive experience for the user, allowing them to complete tasks without frustration.
What Are the Key Differences Between UI and UX Design?
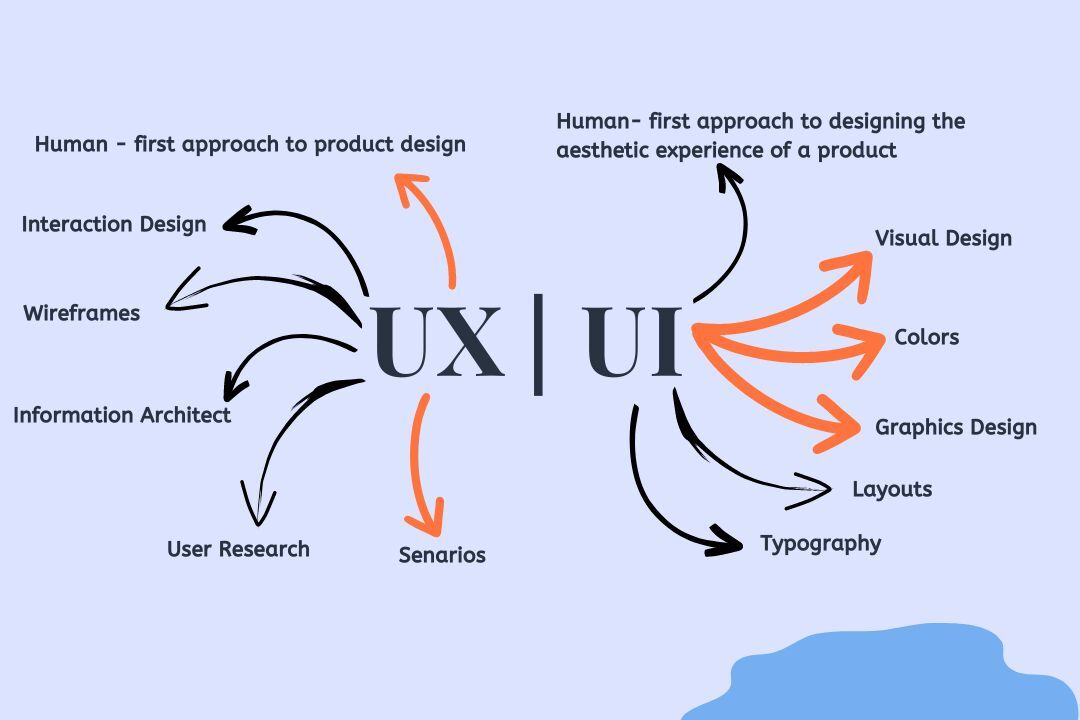
UX design mostly deals with the user’s entire journey to solve a problem. On the other hand, UI design is focused on how the product looks and feels when the problem is being solved.
Tools: UI designers use tools like Sketch, Flinto, Principle, and InVision for collaborative image designing. UX designers use wireframe-based prototyping tools like Mockplus.
Artistic Component: UI designers have to include an artistic component in their design since it is related to what the end user sees, hears, and feels. UX design has more of a social component, as it needs to understand what a user wants to experience in the end product.
Dain Miller used to say:
“UI is the saddle, the stirrups, and the reins. UX is the feeling you get being able to ride the horse.”
—Dain Miller, Web Developer
What does a UI designer do?
UX designers focus their work on the experience a user has with a product. The goal is to make products that are functional, accessible, and enjoyable to use.
- Designing layouts and properly spacing page elements on a page
- Improving and modernizing existing design environments
- Ensuring designs can adapt to multiple device types (adaptive design)
- Visualizing interactive elements, like buttons, sliders, toggles, icons, drop-down menus, and text fields
- Choosing color palettes, fonts, and typesetting
- Making style guides for consistent brand identity company-wide
- Creating wireframes or high-fidelity (hi-fi) layouts to show what an interface looks like with visual elements and branding included
What does a UX designer do?
UI designers create the graphical portions of mobile apps, websites, and devices—the elements that a user directly interacts with. Unlike UX, which can apply to just about any product or service, the term UI applies exclusively to digital products.
1. Understand the user and the brand. Think about what problem you’re trying to solve for the user (and how this aligns with brand goals).
2. Conduct user research. Identify user needs, goals, behaviors, and pain points. Tools for user research might include surveys, one-on-one interviews, focus groups, or A/B testing. At some companies, a UX researcher leads this process.
3. Analyze what you’ve learned. At this stage, you’ll build user personas based on your research to help you identify the most important elements of the product or service. Start to map out what the user flow will look like.
4. Design. As you begin to build out the design, you’ll create site maps, wireframes, or prototypes to give you and your team a better idea of what the final product will look like. At this stage, a user interface (UI) designer will add visual or interface elements.
5. Conduct user testing. Validate the design by tracking how real users interact with the product or service (usability testing). Identify any problems with the design and develop solutions.
6. Present your work. Deliver the design solution to your client or company.
What skills do UI designers need?
Some hard skills are required to become a UI designer. To expand, UI designers must be up-to-date with the latest trends, techniques, and technologies. As far as graphic design, they must have an understanding of visual design, interface design, brand design, layouts, etc. They must also have proficiency in visual design and wireframing tools (Adobe XD, Figma, Sketch, Mockplus). Experience working in Agile/Scrum development processes and learning HTML, CSS, and Javascript for rapid prototyping are also helpful.
Teamwork and communication — The UI designer must be a team player. They work closely with product designers and web developers, so they need to communicate clearly in order to create a successful final product.
Adaptability — Technology is constantly changing. Good UI designers embrace change and stay on top of industry trends in order to continuously improve their products and services.
What skills do UX designers need?
Being that the work is quite specific, UX designers need a technical skill set, like design and prototyping with tools like Sketch, Figma and Adobe XD. They also need to understand the design thinking process in order to participate in all aspects of the design process.
Research — Research is a key UX design skill. Designers must make actionable insights from the data they collect, both in the initial phases and when testing with real people.
Problem-solving — UX designers explore many different approaches to solving a specific user problem in a process known as “ideate.” They not only solve problems during initial prototyping, but they constantly develop and improve products or services as needed to make them more user-friendly.
Communication — Communication is crucial as UX design is a highly collaborative process. UX designers also need a level of empathy that lets them look at a product from the user’s point of view. This includes understanding the user’s needs and goals when using the product and being able to communicate them clearly within the team and to stakeholders.
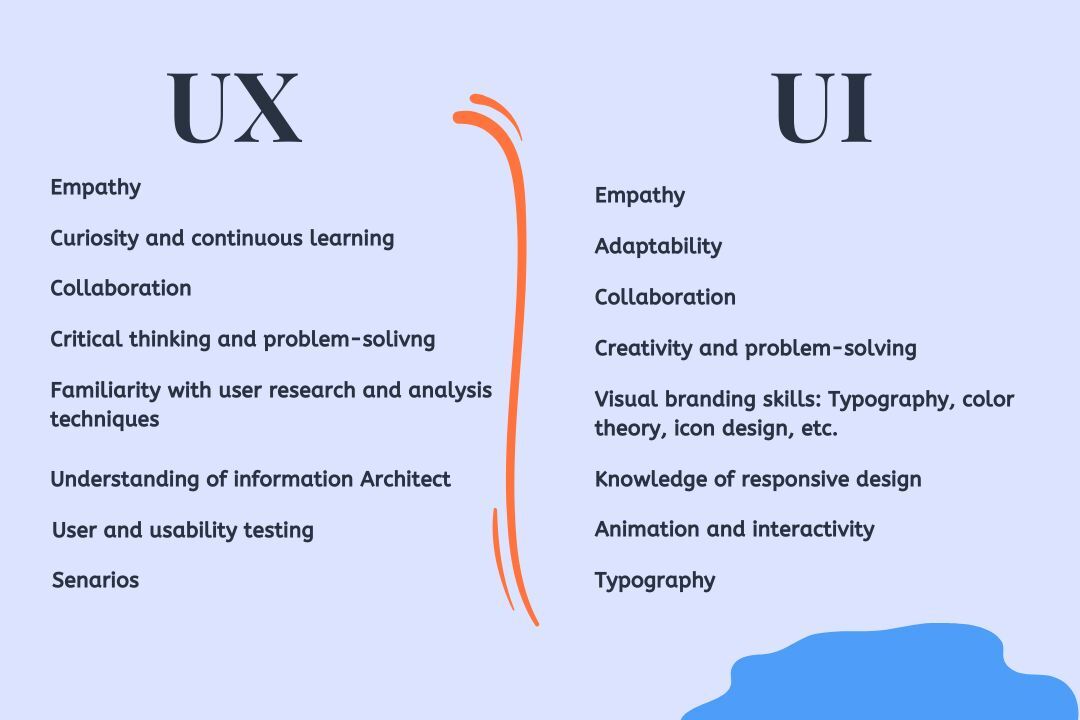
How Do UI/UX Designers Work Together?
While UI design and UX design require very different skill sets, they are both important components that must work simultaneously to give the best experience to end users.
Your app offers something that your target audience needs and wants; however, when they download it, they find that the text on each screen is barely legible (think yellow text on a white background). What’s more, the buttons are too close together; they keep hitting the wrong button by mistake! This is a classic case of bad UI destroying what would have been good UX.
A UI design might be beautiful, but it can be clunky and confusing to navigate without a good UX design. On the other hand, the user experience of a product can be flawless, but it is nothing without a good looking user interface.
Any frontend development and design process should start with understanding the needs of the user. UX and UI designers should work in collaboration with other developers, managers, and product owners to understand what the end product should be able to do, how it should feel, and what it should look like.
A quote from Steve Jobs that reads, “Design is not just what it looks like and feels like. Design is how it works.”
What are FAQs about UX/UI design?
Is UX/UI in demand?
UX/UI design skills are highly sought after. In fact, they are some of the top skills in 2021 as cited by LinkedIn. As more people spend more time online, businesses are shifting to be able to serve these users. This means companies are increasingly looking for UX, UI, and product designers.
Does UX design require coding?
UX design does not require coding. However, it’s always helpful to have a basic understanding of code, including HTML and CSS. Knowing a little code helps you communicate with developers and develop realistic expectations. There are also instances in which learning to code may benefit your career, such as at a startup, where you may be required to perform multiple roles.
How can I get into UX/UI design?
You can get into UX/UI design by reading articles, watching videos, and reading popular books. Although you can continue to self-teach, a bootcamp is a great option. At a bootcamp, you will quickly learn the skills you need in a simulated work environment, build a design portfolio, and receive career coaching.
Is UX/UI design a good career?
Yes, both UX and UI design are good career paths. They are both in-demand careers that pay well with a good job outlook. They are also great for the altruistic because you can do what you love while helping people with everyday challenges! Schedule a 10-minute chat with admissions to learn more about the product design program at Flatiron School.
Related Post
Successful e-commerce websites have one thing in common. They not only have a se...
Nowadays when every business, whatever its size, is connected to the Internet, t...
San Francisco: To give group on its app a better control over how members engage...